Action Plan for CFOs: How to Get Ready for Global Minimum Tax Implementation
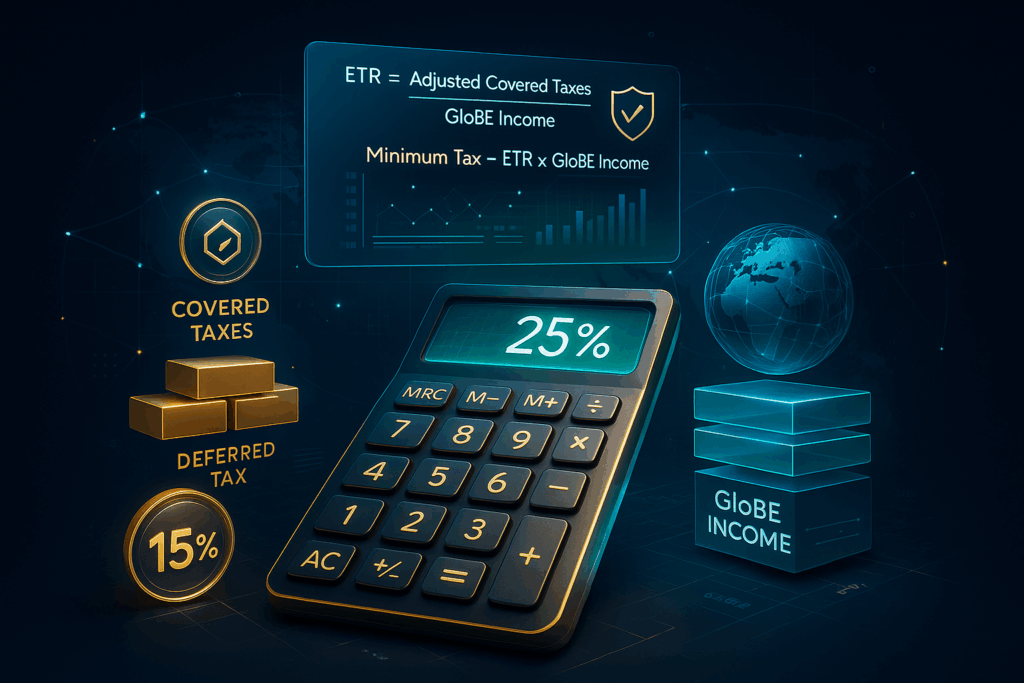
Introduction With the OECD’s Pillar Two Global Minimum Tax (GMT) moving from policy discussion to on-the-ground implementation, CFOs across the world especially in MENA, Europe, Africa, and Asia are facing one of the biggest tax transformations in decades. The Global Minimum Tax introduces a jurisdiction-based 15% effective tax rate (ETR), requiring unprecedented visibility into data, […]
Action Plan for CFOs: How to Get Ready for Global Minimum Tax Implementation Read More »